calf diphtheria prevention
Move the dairy calf from its calving area and place it in its permanent preweaning home as soon as possible after birth. Affected calves might cough and could be either bright and well with minimal discharge from their noseeyes or they could be very sick.
Calf Diphtheria Symptoms And Treatment Vetmedicine Bd
Calf hutches provide good accommodation with respect to the prevention of respiratory diseases but must be.

. It can lead to difficulty breathing heart failure paralysis and even death. A post-mortem can confirm the ulcerative nature of the disease particularly in calves with the laryngeal form. If hes struggling for breath staggering from lack of oxygen you need to slice through the windpipe below the larynx carefully cutting between the ribs of cartilage surrounding the windpipe with a clean sharp knife for the calf to breathe.
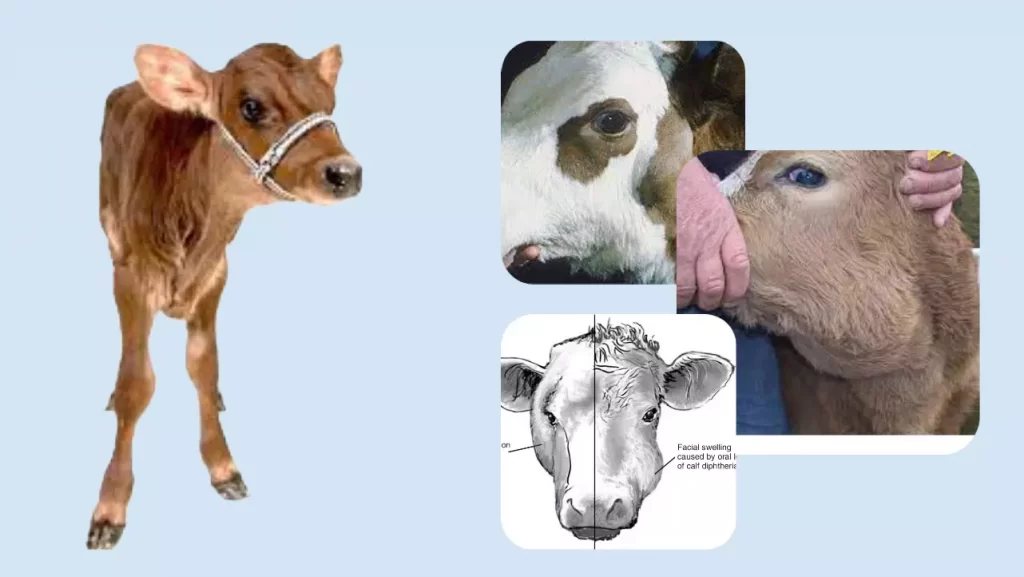
Avoid crowding and competition particularly before during and immediately after weaning. Calf diphtheria is typically seen as ulcerative necrosis of the cheek which appears as an external swelling on the side of the mandible or a lesion on the tongue. This report serves as a reminder that even though it occurs infrequently cases of calf diphtheria are still diagnosed.
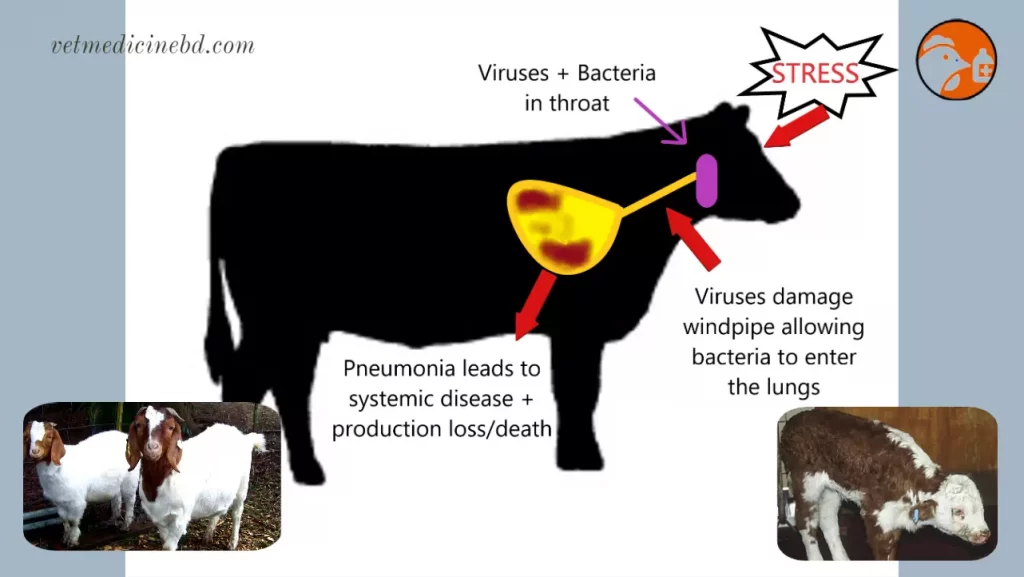
Improved husbandry ventilation and good nursing care can all reduce risks of pneumonia as well as ensuring that young animals receive appropriate amounts. Provide calf starter within the first week of life. Dirty buckets and contaminated water drinkers constitutes an important source of infection not only for pathogens causing diarrhoea but diseases such as calf diphtheria.
Die Inzidenz kann mithilfe der epidemischen Überwachung abgeschätzt werden. There are no specific preventative measures for calf diphtheria. The best method of preventing diphtheria is to prevent any oral injury from occurring.
Treatment with anaerobic specific antibioticsshould commence immediately either parenterally or orally for three to five days. Make adjustments in volume or number of feedings for cold temperatures or illness. Bringing people to the ranch virtually November 30 2016 Beef Cattle.
Navel ill and calf diphtheria. A bacterial infection of the mouth in bucket-fed calves 2018-05-30 Calf diphtheria is a bacterial infection of the mouth in calves. If animals are closely confined the spread of this infectious disease can be prevented by thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting all calf feeders.
It causes necrosis of the mucus membrane of the larynx especially the lateral arytenoids cartilage and adjacent structures. Early prompt treatment is important as early treatment is much more effective Separate the infected animals and isolate them Antibiotics and pain killers are effective in most cases The laryngeal form is much more resistant to treatment. In the laryngeal form treatment should continue for longer.
Learn more about diphtheria vaccination including who should get which vaccine s. Veterinary attention is essential when infection causes respiratory distress. In dieser Hinsicht sollte die Prävention bei jedem Menschen an erster Stelle stehen um keine Diphtherie zu entwickeln.
Es umfasst die Sammlung von Informationen über die Prävalenz der Krankheit den Schweregrad der Impfung und die Merkmale von Veränderungen der. CDC recommends vaccines for infants children teens and adults to prevent diphtheria. The diagnosis of calf diphtheria is usually based on the clinical signs.
An antibiotic alone will not work as. Edema and inflammation of the larynx occurs. Various treatments for calf diphtheria December 8 2016 Cattlemans Corner.
The animal should be isolated from the herd and cross contamination between its and others feed buckets and equipment should be prevented. A producer may need to slice through the windpipe below the larynx creating an opening for the calf to breathe. Examination Bacteriology can be also useful.
Since the loud breathing makes diphtheria easy to identify the next step is to treat these calves in a timely manner. Fluid therapy is the most effective treatment strategy. Calf diphtheria is often treated with daily procaine penicillin by intramuscular injection for 5 to 7 consecutive days as directed by your veterinary surgeon.
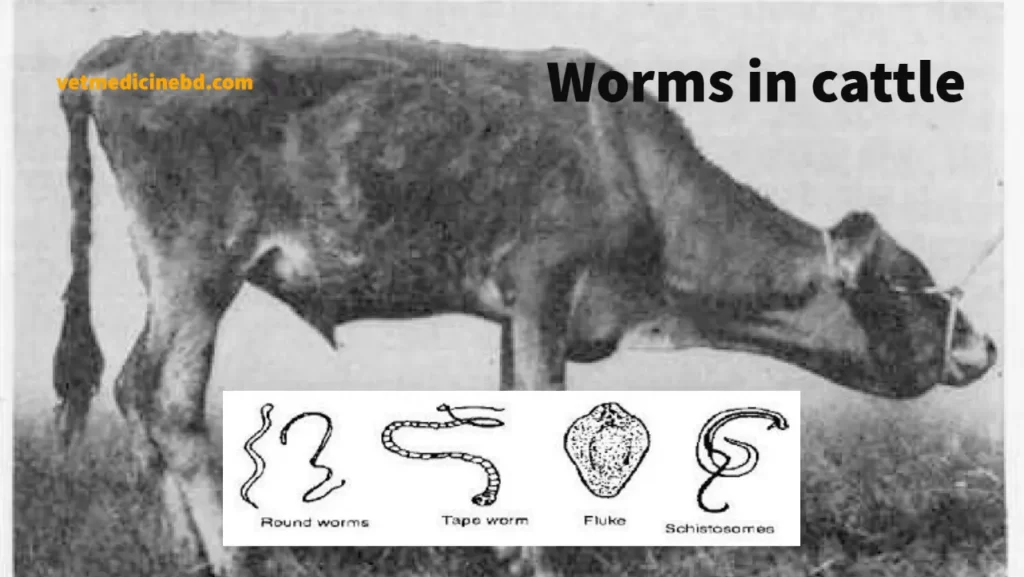
Lungworm Symptoms Sudden sharp coughing Increased breathing rate Many animals may not show any other signs of disease Severely affected animals show weight loss lethargy and difficulty breathing Cause Lungworm disease is caused by a parasite called Dictyocaulus viviparous. DTaP Tdap DT and Td. As with all animal diseases prevention is better than cure and an effective veterinary herd health plan is essential to maintain health and prevent costly diseases.
It is generally associated with poor hygiene in housed bucket reared calves less than three months of age. That means carefully cutting between the ribs of cartilage surrounding the windpipe with a very clean sharp knife. Diphtheria is most common in calves but older animals are sometimes affected.
This can be difficult but a good way of doing this would be to keep calves away from thistles bushes and other sharp objects that they might try to put in their mouths like loose screws or nails. DTaP and Tdap also help prevent pertussis whooping cough. About Diphtheria Vaccination For Clinicians Laboratory.
In the United States there are four vaccines used to prevent diphtheria. Diphtheria is a serious infection caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make toxin poison. Parenteral antibiotics should be used to control concurrent infections eg.
Prevention It can be difficult to control pneumonia when calves are placed in communal pens. Get veterinary advice Prevention. Calf diphtheria is prevented by strict hygiene.
Other respiratory diseases in your calves may include calf diphtheria calf coughs and lungworm. Early diagnosis treatment and prevention is really important as once the calves are sick the damage to the lungs can be permanent meaning the calves will. You need to slice through the windpipe below the larynx carefully cutting between the ribs of cartilage surrounding the windpipe with a clean sharp knife for the calf to breathe through.
Because it is unlikely that a calf will never cut its mouth we also suggest that you keep all feeding. For one-off cases rule out other problems such as BVD and foreign bodies by getting your vet to do a thorough oral. Poor hygiene with respect to feeding equipment eg.
Diphtheria is most common in calves but older animals are sometimes affected. Young calves must be examined daily to identify early stages of the disease. Called necrotic laryngitis or calf diphtheria also referred to as barker calves the initiating cause is usually a throat abrasion caused by rough feed or an oral ulcer.
Diphtheria is seen most commonly in calves but older animals are not completely immune. Each of these vaccines prevents diphtheria and tetanus.

Cattle Diseases Vetmedicine Bd

Nadis National Animal Disease Information Service

Livestock Diseases Ppt Download

African Farm Resource Centre Calf Diseases Diphtheria What Is Calf Diphtheria There Are Two Forms Of Calf Diphtheria The Most Common Is An Acute Oral Mouth Infection Usually Seen In Calves

Nadis National Animal Disease Information Service

Respiratory Disease In Youngstock Vetsouth
Calf Diphtheria Symptoms And Treatment Vetmedicine Bd

Calf Diphtheria Symptoms And Treatment Vetmedicine Bd

Nadis National Animal Disease Information Service

Care Of The Newborn Calf Mini Review Pashudhan Praharee

Various Treatments For Calf Diphtheria Grainews

Nadis National Animal Disease Information Service

Calf Diphtheria Symptoms And Treatment Vetmedicine Bd

African Farm Resource Centre Calf Diseases Diphtheria What Is Calf Diphtheria There Are Two Forms Of Calf Diphtheria The Most Common Is An Acute Oral Mouth Infection Usually Seen In Calves
Calf Diphtheria Symptoms And Treatment Vetmedicine Bd

Dealing With Diphtheria In Calves Grainews

African Farm Resource Centre Calf Diphtheria Necrobacillosis There Are Two Forms Of Calf Diphtheria The Most Common Is An Acute Oral Mouth Infection Usually Seen In Calves Less Than 3 Months


Comments
Post a Comment